Configuring SRTP
The device supports Secured RTP (SRTP) according to RFC 3711. SRTP is used to encrypt RTP and RTCP transport for protecting VoIP traffic. SRTP requires a cryptographic key exchange mechanism to negotiate the keys. To negotiate the keys, the device supports the Session Description Protocol Security Descriptions (SDES) protocol (according to RFC 4568), or Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) protocol for SBC calls. For more information on DTLS, see SRTP using DTLS Protocol.
Key exchange is done by adding the 'a=crypto' attribute to the SDP. This attribute is used (by both sides) to declare the various supported cipher suites and to attach the encryption key. If negotiation of the encryption data is successful, the call is established. Typically, 'a=crypto' is included in secured media (RTP/SAVP). However, there is also support for including 'a=crypto' in non-secured media (RTP/AVP). In such cases, the media is handled as if the device received two identical media: one secured and one not.
SRTP supports the following cipher suites (all other suites are ignored):
|
■
|
AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32 |
|
■
|
AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80 |
|
■
|
ARIA_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80
|
|
■
|
ARIA_CM_192_HMAC_SHA1_80
|
|
■
|
AES_256_CM_HMAC_SHA1_32 (RFC 6188) |
|
■
|
AES_256_CM_HMAC_SHA1_80 (RFC 6188) |
When the device is the offering side (SDP offer), it can generate a Master Key Identifier (MKI). You can configure the MKI size globally, using the [SRTPTxPacketMKISize] parameter, or per SIP entity, using the IP Profile parameter 'MKI Size'. The length of the MKI is limited to four bytes. If the remote side sends a longer MKI, the key is ignored.
|
●
|
Gateway application: The device only initiates the MKI size.
|
|
●
|
SBC application: The device can forward MKI size transparently for SRTP-to-SRTP media flows or override the MKI size during negotiation (inbound or outbound leg).
|
The key lifetime field is not supported. However, if it is included in the key it is ignored and the call doesn't fail. For SBC calls belonging to a specific SIP entity, you can configure the device to remove the lifetime field in the 'a=crypto' attribute, using the IP Profile parameter 'SBC Remove Crypto Lifetime in SDP'.
For SDES, the keys are sent in the SDP body ('a=crypto') of the SIP message and are typically secured using SIP over TLS (SIPS). The encryption of the keys is in plain text in the SDP. The device supports the following session parameters:
Session parameters should be the same for the local and remote sides. When the device is the offering side, the session parameters are configured by the following parameters - 'Authentication on Transmitted RTP Packets', 'Encryption on Transmitted RTP Packets, and 'Encryption on Transmitted RTCP Packets'. When the device is the answering side, the device adjusts these parameters according to the remote offering. Unsupported session parameters are ignored, and do not cause a call failure.
Below is an example of crypto attributes usage:
a=crypto:1 AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80 inline:PsKoMpHlCg+b5X0YLuSvNrImEh/dAe
a=crypto:2 AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
inline:IsPtLoGkBf9a+c6XVzRuMqHlDnEiAd
The device also supports symmetric MKI negotiation, whereby it can forward the MKI size received in the SDP offer 'a=crypto' line in the SDP answer. You can enable symmetric MKI globally, using the global parameter [EnableSymmetricMKI], or per SIP entity, using the IP Profile parameter 'Symmetric MKI' and for SBC calls 'SBC Enforce MKI Size'. For more information on symmetric MKI, see Configuring IP Profiles.
You can configure the enforcement policy of SRTP, by the [EnableMediaSecurity] parameter and IP Profile parameter 'SBC Media Security Mode' parameter for SBC calls. For example, if negotiation of the cipher suite fails or if incoming calls exclude encryption information, the device can be configured to reject the calls.
You can also enable the device to validate the authentication of packets for SRTP tunneling for RTP and RTCP. This applies only to SRTP-to-SRTP SBC calls and where the endpoints use the same key. This is configured using the 'SRTP Tunneling Authentication for RTP' and 'SRTP Tunneling Authentication for RTCP' parameters.
|
●
|
When SRTP is used, channel capacity may be reduced.
|
The procedure below describes how to configure SRTP through the Web interface.
|
➢
|
To enable SRTP globally (for all calls): |
|
1.
|
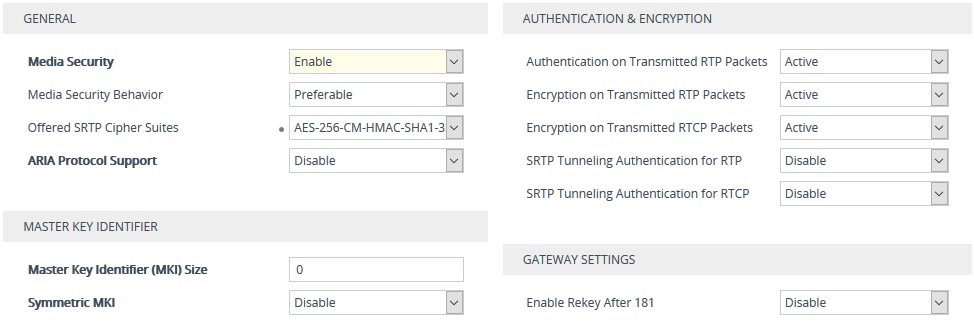
Open the Media Security page (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > Media folder > Media Security). |
|
2.
|
From the 'Media Security' drop-down list [EnableMediaSecurity], select Enable to enable SRTP. |
|
3.
|
From the 'Offered SRTP Cipher Suites' drop-down list [SRTPofferedSuites], select the supported cipher suite. |
|
4.
|
Configure the other SRTP parameters as required. |
